Advantages And Disadvantages Of Serial And Parallel Data Transmission
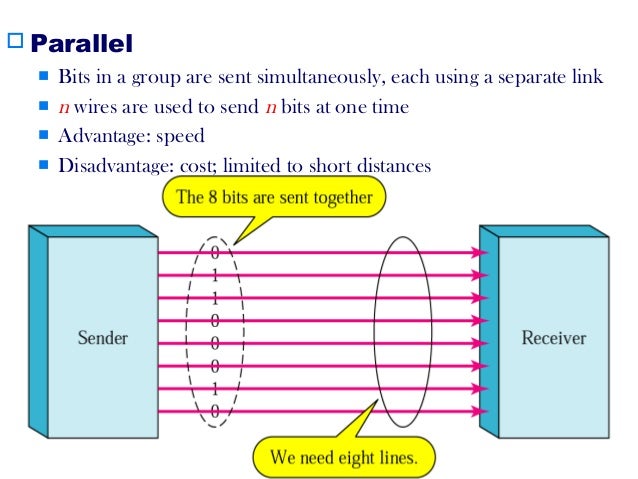
Parallel and serial data transmission are most widely used data transfer techniques. Parallel transfer have been the preferred way for transfer data. But with serial data transmission we can achieve high speed and with some other advantages. In parallel transmission n bits are transfered simultaneously, hence we have to process each bit separately and line up them in an order at the receiver. Hence we have to convert parallel to serial form. This is known as overhead in parallel transmission. Signal skewing is the another problem with parallel data transmission.
Serial transmission occurs in one of three ways: asynchronous, synchronous, and isochronous. Parallel Transmission Binary data, consisting of 1 s and 0 s, may be organized into groups of n bits each.
In the parallel communication, n bits leave at a time, but may not be received at the receiver at the same time, some may reach late than others. To overcome this problem, receiving end has to synchronize with the transmitter and must wait until all the bits are received. The greater the skew the greater the delay, if delay is increased that effects the speed. Another problem associated with parallel transmission is crosstalk. When n wires lie parallel to each, the signal in some particular wire may get attenuated or disturbed due the induction, cross coupling etc. As a result error grows significantly, hence extra processing is necessary at the receiver.
Serial communication is full duplex where as parallel communication is half duplex. Which means that, in serial communication we can transmit and receive signal simultaneously, where as in parallel communication we can either transmit or receive the signal. Hence serial data transfer is superior to parallel data transfer. Practically in computers we can achieve 150MBPS data transfer using serial transmission where as with parallel we can go up to 133MBPS only. The advantage we get using parallel data transfer is reliability. Serial data transfer is less reliable than parallel data transfer. How do you convert a XOR gate into a buffer and a inverter (Use only one XOR gate for each)?
Implement an 2-input AND gate using a 2x1 mux. What is a multiplexer? A multiplexer is a combinational circuit which selects one of many input signals and directs to the only output.
What is a ring counter? Dolzhnostnaya instrukciya pedagoga psihologa v shkole respubliki kazakhstan. A ring counter is a type of counter composed of a circular shift register.
The output of the last shift register is fed to the input of the first register. For example, in a 4-register counter, with initial register values of 1100, the repeating pattern is: 1100, 0110, 0011, 1001, 1100, so on. Compare and Contrast Synchronous and Asynchronous reset.
Synchronous reset logic will synthesize to smaller flip-flops, particularly if the reset is gated with the logic generating the d-input. But in such a case, the combinational logic gate count grows, so the overall gate count savings may not be that significant. The clock works as a filter for small reset gl. >> >> >> >> In Verilog HDL a module can be defined using various levels of abstraction. There are four levels of abstraction in verilog.